RDS Serverless Cluster: Available, Reliable, Financiable
✨Aurora Serverless databases offer flexible scaling, automatic maintenance, and cost savings. They adapt resources in real-time, reduce expenses by pausing during idle periods, and ensure high availability. With simplified setup and management, developers can focus on their applications without worrying about capacity planning. 💰🔄
Table of contents
Use Cases
The AWS RDS Aurora database cluster setup can be utilized in various scenarios, including:
Effortless Scalability for Startups: Startups effortlessly scale their databases with RDS Aurora serverless architecture and Terraform. Automatic scaling handles unpredictable growth, while streamlined resource management and cost-effective scaling optimize operations. Terraform simplifies disaster recovery, provisioning and configuration, enabling startups to establish reliable, scalable infrastructure for hassle-free growth.
Highly Available Applications: Deploying an RDS Aurora database cluster ensures high availability for your applications. By leveraging automatic replication and failover capabilities, you can maintain uninterrupted access to your database even in the event of a failure.
Multi-Region Data Replication: RDS Aurora supports cross-region replication, enabling you to replicate your database across multiple AWS regions. This provides disaster recovery capabilities and allows you to serve your customers from different geographical locations with low latency.
Requirements
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| Terraform | >= 1.0 |
| AWS CLI | >= 2.0 |
| OpenVPN | >= 2.5 |
Installation
Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/BlackArrowGang/Arsenal.git
Go to the solution directory
cd /Arsenal/quiver/aws-serverless-rds-cluster
Install terraform modules
terraform init
Usage
Note: It might take a few minutes to fully create.
To use this code, follow these steps:
Modify Code
- Set the desired profile, region, vpc and database config on the locals section inside the main.tf file
- Add your VPN server and client certificate ARN’s.
Terraform Setup
- Run the following commands
terraform plan
terraform apply
Connect to VPN
- Desktop Client
- Refer to this AWS documentation for detailed instructions on setting up the vpn certificates on your account.
- Then go to the section named “Exporting and configuring the VPN client configuration file” of this other AWS documentation to connect with your vpn client.
- Linux Command
sudo openvpn --config config.ovpn
Connect To Database Cluster
- Now that you are connected to the VPN, you have access to the database cluster and can connect to it, be sure to connect via the url endpoint of any database instance
How It Works
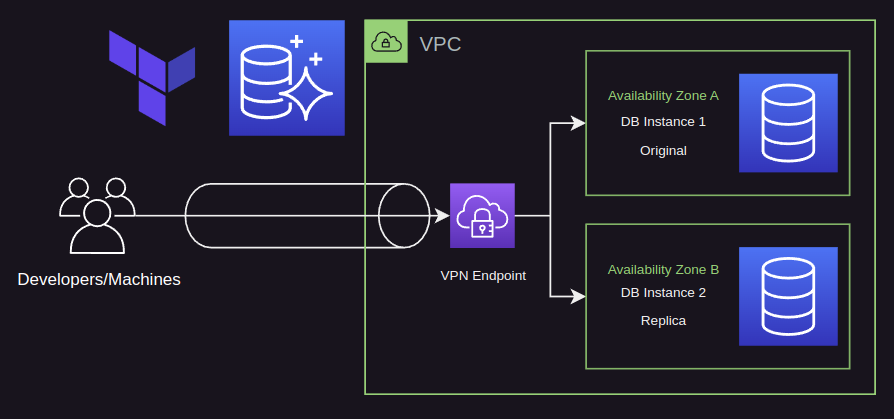
VPC Module:
- The VPC module creates a custom VPC with the CIDR block “142.32.0.0/16” across two availability zones (“us-east-2a” and “us-east-2b”).
- It sets up two private subnets with CIDR blocks “142.32.1.0/24” and “142.32.2.0/24”.
- Additionally, it creates database subnets with CIDR blocks “142.32.3.0/24” and “142.32.4.0/24”.
Aurora PostgreSQL RDS Module:
- The RDS module deploys an Aurora PostgreSQL database cluster within the VPC.
- It utilizes the “db.serverless” instance class with two instances.
- Serverless scaling is configured with a minimum capacity of 0.5 and a maximum capacity of 1.
- The database is connected to the VPC, a database subnet group, and the “resource_access_security_group” security group.
- Other configurations include monitoring, skipping the final snapshot, applying changes immediately, and encrypting the storage.
Security Group Modules:
- The “vpn_access_security_group” module is responsible for creating a security group named “vpn_access” that allows connection to the VPN.
- The “resource_access_security_group” module creates a security group named “resource-access” that allows access to AWS resources.
- The “resource_access_security_group” module enables communication between networks within the VPC and allows outbound TCP traffic on port 5432 to itself.
Client VPN Endpoint Configuration:
- The server certificate ARN.
- A client CIDR block of “192.168.128.0/22”.
- The VPN endpoint is associated with the VPC and the “vpn_access_security_group” and “resource_access_security_group” security groups.
- Certificate-based authentication is configured with the root certificate chain ARN.
Client VPN Authorization Rule:
- An authorization rule is set up to allow VPN access to the entire VPC or a specific CIDR block.
- The authorization rule is associated with the client VPN endpoint.
Client VPN Network Associations:
- The client VPN endpoint is associated with the private subnets the VPC to enable VPN connectivity.
Support
If you encounter any issues or need assistance setting things up, Hire us and we can do it for you.
Want to try things for yourself?, checkout our github repository Arsenal.
To get started, you can visit our website blackarrowgang.com to explore our services and schedule a meeting with our team. We are committed to providing you with the necessary support and guidance.
Dont forget to checkout our youtube channel Black Arrow Gang, where we will showcase the functionality of this services in the future.
And if you are feeling generous you can go ahead and buy us a cup a coffee.
